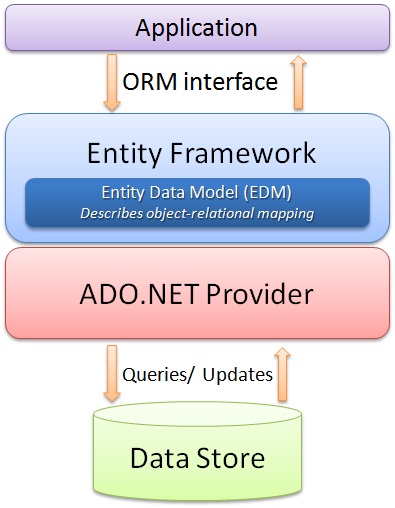
Entity Framework is an Open-Source Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) Framework for .NET applications that enables .NET developers to work with relational data using domain-specific objects without focusing on the underlying database tables and columns where actually the data is stored. That means the Entity Framework eliminates the need for writing the data-access code that developers usually need to write.

Official Definition: “Entity Framework is an object-relational mapper (O/RM) that enables .NET developers to work with a database using .NET objects. It eliminates the need for most of the data-access code that developers usually need to write.â€
What is an Object-Relational Mapping Framework?
Object Relational Mapping framework automatically creates classes based on database tables, and vice versa is also true, that is, it can also automatically generate the necessary SQL to create database tables based on classes. The following diagram illustrates where the Entity Framework fits into our application.
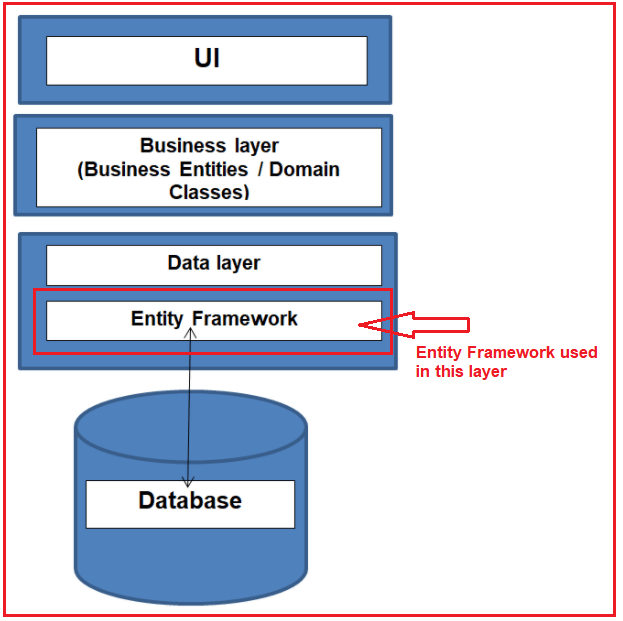
The above diagram shows that the Entity Framework fits between the business entities (i.e. the domain classes) and the database. It saves the data in the database which are stored in the properties of the business entities (domain classes) and also retrieves the data from the database and converts it to business entities objects automatically.
Lets understand what an entity framework can do for us with an example.
Assume we have the following 2 tables (Departments and Employees).

We want to display the data from both tables (Departments and Employees) in a console application as shown below.

To achieve this
- We need to create Department and Employee classes
- We need to write ADO.NET code to retrieve the data from the database
- Once the data is retrieved we need to create Department and Employee objects and populate them with the retrieved data.
But Entity Framework can do all of the above automatically for us if we provide the necessary database schema to the Entity Framework. Let us understand this step by step of how to achieve the same using Entity Framework.
Step1: Creating the Database Schema
Please use the below SQL script to create the database (EF_Demo_DB), tables (Departments and Employees), and populate the tables with sample data.
Step2: Create a Console Application
Once the database is ready, in the next step, create a new “Console Application†with the name EFDemo as shown in the below image.

Step3: Adding ADO.NET Entity Data Model
Once you create the Console Application, next we need to add ADO.NET Entity Data Model. To do so, Right-click on the project in solution explorer and select Add => New Item, and then click on Data Section from the left side panel and choose ADO.NET Entity Data Model from the middle panel, Change the name from Model1 to EmployeeDataModel and click on the Add button as shown in the below image.

Once you click on the Add button, it will open the Choose Data Model wizard as shown below. From this window select “EF Designer from database†and click on the Next button as shown in the below image. Here, select the “EF Designer from database†option as we are going to use the Entity Framework database First Approach.

Once you click on the Next button, It will open choose your data connection wizard as shown below. From this window click on the New Connection button as shown in the below image.

Once you click on the New Connection button, it will open a popup for providing the database details as shown below. From this connection properties screen,
- Select “Microsoft SQL Server†as Data source, and “.Net Framework Data Provider for SQL Server†option from the “Data provider†drop-down list. Click Continue.
- On the “Connection Properties†screen, specify SQL Server Name.
- Specify the Authentication you want to use.
- Select the database from the “Select or enter a database name†drop-down list.
- Finally “Test connection†and click “OKâ€

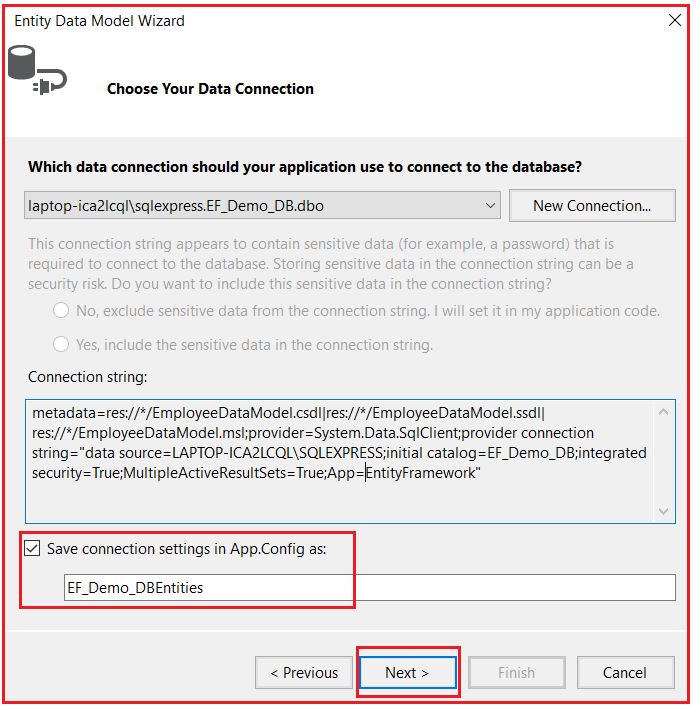
Once you click on the OK button, you will be back on to the “Choose Your Data Connection†window as shown below. Make sure the “Save entity connection settings in App.Config as†checkbox is selected and change the name of the connection string to EF_Demo_DBEntities and then Click on the “Next†button as shown in the below image.
Once you click on the Next button, it will open a popup asking you to choose the Entity Framework version as shown below. From this window, select Entity Framework 6.x and click on the Next button as shown in the below image.

Once you click on the Next button, it will open Choose Your Database Objects as shown below. From the below window, select “Departments†and “Employees†tables. Change the Model Namespace to “EmployeeModel†and click on the “Finish†button as shown in the below image.

Once you click on the “Finish†button, it should generate the EmployeeDataModel.edmx file.

Following is the structure of the EDMX file.

The Entity Framework Create Employee and Department classes automatically based on the Employees and Departments Tables. Tables are mapped to classes and columns are mapped to class properties.
Using Entity Framework:
Now copy and paste the following code in the main method of program class as shown below. Here, in this Video, I am not going to explain the code. Here, I just want to show how to use Entity Framework. From our next Video onwards, I am going to explain each and everything in detail.
Run the application and notice that departments and employees data are displayed as expected. We have achieved all this without writing a single line of ADO,NET code. If this is not clear at this moment how it works, then dont worry we will discuss each and everything in detail in our upcoming Videos.
Entity Framework Features:
- Cross-platform: EF Core is a cross-platform framework which means it can run on Windows, Linux, and Mac operating systems.
- Modeling: EF (Entity Framework) creates an EDM (Entity Data Model) based on POCO (Plain Old CLR Object) entities with get/set properties of different data types. It uses this model also when querying or saving entity data to the underlying database.
- Querying: EF allows us to use LINQ queries (C#/VB.NET) to retrieve data from the underlying database. The database provider will translate this LINQ queries to the database-specific query language (e.g. SQL for a relational database). EF also allows us to execute raw SQL queries directly to the database.
- Change Tracking: EF keeps track of changes that occurred to instances of our entities (Property values) that need to be submitted to the database.
- Saving: EF executes INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE commands to the database based on the changes that occurred to our entities when we call the SaveChanges() method. EF also provides the asynchronous SaveChangesAsync() method.
- Concurrency: EF uses Optimistic Concurrency by default to protect overwriting changes made by another user since data was fetched from the database.
- Transactions: EF performs automatic transaction management while querying or saving data. It also provides options to customize transaction management.
- Caching: EF includes the first level of caching out of the box. So, repeated querying will return data from the cache instead of hitting the database.
- Built-in Conventions: EF follows conventions over the configuration programming pattern, and includes a set of default rules which automatically configure the EF model.
- Configurations: EF allows us to configure the EF model by using data annotation attributes or Fluent API to override default conventions.
 Best resource for Online free Education
Best resource for Online free Education