Decision Tree is a decision-making tool that uses a flowchart-like tree structure or is a model of decisions and all of their possible results, including outcomes, input costs, and utility. Decision-tree algorithm falls under the category of supervised learning algorithms. It works for both continuous as well as categorical output variables.

The branches/edges represent the result of the node and the nodes have either:
- Conditions [Decision Nodes]
- Result [End Nodes]
The branches/edges represent the truth/falsity of the statement and take makes a decision based on that in the example below which shows a decision tree that evaluates the smallest of three numbers:
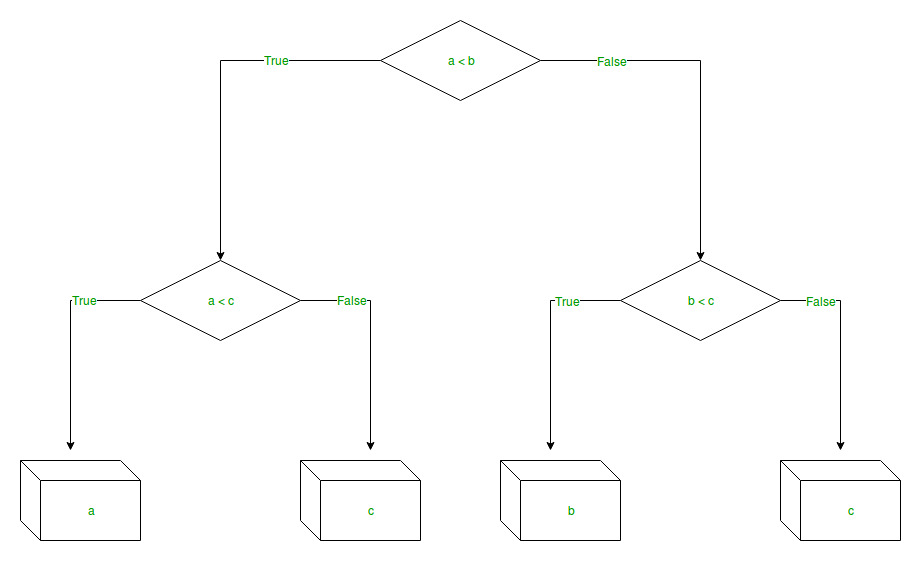
Decision Tree Regression:
Decision tree regression observes features of an object and trains a model in the structure of a tree to predict data in the future to produce meaningful continuous output. Continuous output means that the output/result is not discrete, i.e., it is not represented just by a discrete, known set of numbers or values.
 Best resource for Online free Education
Best resource for Online free Education